Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is
a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver, sometimes leading to
severe liver damage. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) spreads through contaminated
blood. Until recently, the treatment of hepatitis C required weekly injections
and medications that many people infected with HCV could not take due to other
health problems or unacceptable side effects.
This is
changing. Today, chronic HCV is generally treatable with oral medications every
other day for 2-6 months. Half of people with HCV do not know they are
infected, mainly because they have no symptoms, which can take decades.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Long-term
infection with hepatitis C virus is known as chronic hepatitis C. Chronic
hepatitis C is usually a "silent" infection for many years, until the
virus damages the liver enough to cause signs and symptoms of liver disease.
Signs and
symptoms include:
- Bleeding easily
- Poured gently
- Fatigue
- Poor appetite
- Yellow discoloration of skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Dark urine
- Irritated skin
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
- Swelling of the legs
- Weight loss
- Confusion, sleepiness, and prone speech (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Spider blood vessels on the skin (spider angiomas)
Causes of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
infection is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection spreads when
blood contaminated by the virus enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person.
Globally, HCV
exists in several distinct forms, known as genotypes. Seven distinct HCV
genotypes and more than 67 subtypes have been identified. The most common HCV
genotype in the United States is type 1.
Although
chronic hepatitis C follows a similar course, regardless of the infectious
virus genotype, treatment recommendations vary according to the viral genotype.
- Sharing of injectable drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have an HIV infection, multiple partners or having hard sex
- Be blocked by infected needles
- Birth: a mother can pass it on to a child
- Sharing personal care items, such as toothbrushes, razor blades and nail clippings
- Get a tattoo or piercing with dirty equipment
Stages of Hepatitis C
Incubation Period.
This is the
time between the first exposure at the beginning of the disease. It may take 14
to 80 days, but the average is 45
Acute Hepatitis C.
This is a short-term disease that lasts for
the first 6 months after the virus has entered your body. Later, some people
who have it will get rid of the virus or eliminate the virus itself.
Chronic Hepatitis C.
If your body does not clear the virus after 6
months, it becomes a long-term infection. This can lead to serious health
problems, such as liver cancer or cirrhosis.
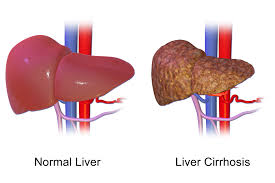 Cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis.

This disease
leads to inflammation that replaces healthy liver cells with scar tissue over
time. It usually takes about 20-30 years for this to happen, although it can be
faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
Liver Cancer.
Cirrhosis makes
liver cancer more expected. Your doctor will make sure you have regular
screening because there are usually no symptoms.
Complications of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C infection that continues for many years can cause significant complications, such as:
Cirrhosis
After
decades of hepatitis C infection, cirrhosis can develop. Scars in the liver
make the functioning of the liver difficult.
Liver cancer.
A
small number of people with hepatitis C infection can develop liver cancer.
Liver Failure
Advanced cirrhosis can cause the liver to stop working.
Prevention from Hepatitis C
Prevent
yourself from hepatitis C infection by taking the following precautions:
- Stop using illicit drugs, especially if you inject them. If you use illicit drugs, ask for help.
- Pay attention to body piercing and tattooing. If you choose to suffer from piercings or tattoos, look for a trusted store. Ask questions in advance about how the equipment is cleaned. Make sure employees use sterile needles. If your employees don't answer your questions, look for another store.
- Practice safer sex. Do not have unprotected sexual relations with multiple partners or partners whose health is uncertain.
Treatment of Hepatitis C
Not everyone
who is infected with hepatitis C will need treatment. For some people, their
immune system may be able to fight the infection well enough to eliminate the
infection from their body. If this is the case, your doctor will probably want
to monitor your liver function with regular blood tests.
For people with
immune systems who are unable to eliminate the infection, there are several
options for the treatment of hepatitis C. Treatment is usually reserved for
people with severe liver scars and scars and there are no other conditions to
prevent the treatment.
Previous
treatment regimens for hepatitis C required weekly injections for 48 weeks.
This treatment had the risk of having significant and sometimes
life-threatening side effects. The new antiviral drugs now have higher cure
rates and fewer adverse reactions. It also requires a shorter treatment period.


I was in severe ribs and stomach pain at about this time last year. And I went to the hospital for treatment and was diagnosed for CHRONIC HEPATITIS B I was told it has no cure and i was so devastated because all hope seems to be lost, some drugs was given me to slowdown the viral load, and it got worse after sometime. I came across Dr. Iyabiye’s recommendation online while studying about the disease, and then I reach out to him just to try but I was taken by surprise. I got completely cured, all the pains were gone and I went back to the hospital for another test and I was tested negative to the disease. Here is the doctor’s contact if interested: iyabiyehealinghome@gmail.com (+234-815-857-7300)
ReplyDelete